Find more information in the General Comments section of the assessment
Find more information in the Rating Validity tab of the assessment
- See More
- See More
- See More
- See More
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor
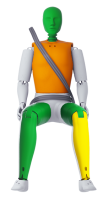 Passenger
Passenger
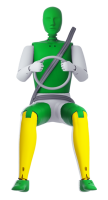 Driver
Driver
 Rear Seat
Rear Seat
 Front Seat
Front Seat
 Car
Car
 Pole
Pole
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor


Passenger
outboard
Fitted to the vehicle as standard
Not fitted to the test vehicle but available as option
Not Available
-
Infants up to 13 kg
-
Infants and toddlers up to 18 kg
-
Toddlers from 9 to 18 kg
-
Toddlers over 18 kg
Easy
Difficult
Safety critical
Not allowed
| Seat Position | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Front | 2nd row | ||
| Passenger | Left | Right | |
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix (Belt) | |||
| Römer King Plus (Belt) | |||
| Römer Duo Plus (ISOFIX) | |||
| Römer KidFix (Belt) | |||
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix & EasyFix (Belt) | |||
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix & EasyFix (ISOFIX) | |||
| BeSafe iZi Kid X3 ISOfix (ISOFIX) | |||
| Maxi Cosi Pearl & Familyfix (ISOFIX) | |||
| Römer KidFix (ISOFIX) | |||
Easy
Difficult
Safety critical
Not allowed
The forfour scored maximum points for its protection of the 1½ year dummy in the crash tests. Forward movement of the head of the 3 year dummy, sat in a forward-facing restraint, was not excessive but neck tensile forces were high and the loading on the chest was also marginally high. In the side impact, both dummies were properly contained within the protective shells of their restraints, minimising the likelihood of dangerous head contact with parts of the vehicle interior. The passenger airbag can be disabled to allow a rearward-facing child restraint to be used in that seating position. Clear information is provided to the driver about the status of the airbag and the system was rewarded. All of the restraint types for which the car is designed could be properly installed and accommodated in the car.
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor

Head Impact 15.2 Pts
Pelvis Impact 2.4 Pts
Leg Impact 6.0 Pts
The bumper scored maximum points for the protection it offered to pedestrians' legs, with good results recorded at all test locations. The protection offered by the front edge of the bumper to a pedestrian's pelvis varied from poor to good. The bonnet surface was predominantly adequate or marginal, while poor protection for a pedestrian's head was recorded only on the stiff windscreen pillars.
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor
| Speed Limitation Function | Manually Set |
| System Name | ESP | |
| Performance | ||
| Applies To | All seats | ||
| Warning | Driver Seat | Front Passenger(s) | Rear Passenger(s) |
| Visual | |||
| Audible | |||
|
|||
Electronic stability control is standard equipment, as is a seatbelt reminder system for the front and rear seats. A driver-set speed limiter is expected to be fitted to most cars sold in Europe, so it was included in the assessment and met Euro NCAP's requirements for systems of this type. A lane departure warning system is also an option but did not qualify for assessment as most cars will not be equipped with it. An autonomous emergency braking system is not available on the forfour.
- Specifications
- Safety Equipment
- Videos
- Rating Validity
Specifications
Tested Model smart forfour 999cc petrol 'passion', LHD
Body Type - 5 door hatchback
Year Of Publication 2014
Kerb Weight 975kg
VIN From Which Rating Applies - all smart forfours including EQ electric variant
Class City and Supermini
Safety Equipment
Note: Other equipment may be available on the vehicle but was not considered in the test year.
Fitted to the vehicle as standard
Fitted to the vehicle as option
Not fitted to the test vehicle but available as option
Not Available
Not Applicable
Videos
Rating Validity






Find more information in the General Comments section of the assessment
Additional tests have been conducted to ensure that the EQ forfour shares the same star rating as the petrol-engined variant originally tested in 2014.
 Share
Share













The passenger compartment remained stable in the frontal impact. Dummy readings indicated good protection of the knees and femurs of the driver and passenger. smart showed that a similar level of protection would be provided to occupants of different sizes and to those sat in different positions. The chest compression of the passenger dummy indicated a marginal level of protection for that body region in the frontal test. In the side barrier impact, protection of all body regions was good apart from the chest, protection of which was adequate. However, in the more severe side pole test, dummy readings of rib compressions highlighted weak chest protection, although the other areas remained well protected. The seats and head restraints provided good protection against whiplash injury in the event of a rear-end collision.