- With standard equipment
- With safety pack
Find more information in the General Comments section of the assessment
Find more information in the Rating Validity tab of the assessment
- See More
- See More
- See More
- See More
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor
 Rear Seat
Rear Seat
 Front Seat
Front Seat
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor


Passenger
outboard
center
Fitted to the vehicle as standard
Not fitted to the test vehicle but available as option
Not Available
-
i-Size CRS
-
ISOFIX CRS
-
Universal Belted CRS
Easy
Difficult
Safety critical
Not allowed
| Seat Position | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front | 2nd row | |||
| Passenger | Left | center | Right | |
| Maxi Cosi 2way Pearl & 2wayFix (i-Size) | ||||
| Maxi Cosi 2way Pearl & 2wayFix (i-Size) | ||||
| BeSafe iZi Kid X2 i-Size (i-Size) | ||||
| Britax Römer TriFix2 i-Size (i-Size) | ||||
| BeSafe iZi Flex FIX i-Size (i-Size) | ||||
| BeSafe iZi Combi X4 ISOfix (ISOFIX) | ||||
| Cybex Solution Z i-Fix (ISOFIX) | ||||
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix (Belt) | ||||
| Maxi Cosi Cabriofix & EasyFix (Belt) | ||||
| Britax Römer King II LS (Belt) | ||||
| Cybex Solution Z i-Fix (Belt) | ||||
Easy
Difficult
Safety critical
Not allowed
In the frontal offset test, dummy readings indicated good or adequate protection for both child dummies. However, analysis of the film revealed that the seat belt had partially slipped off the shoulder of the 10 year dummy and, as a result, the overall score for the test was penalised. In the side barrier impact, dummy readings of accelerations indicated weak protection of the head of the 10 year dummy. Otherwise, protection of all critical body areas was good for both child dummies. The front passenger airbag can be disabled to allow a rearward-facing child restraint to be used in that seating position. Clear information is provided to the driver about the status of the airbag and the system was rewarded. Some universal child restraints were unstable when positioned in the rear centre seating position but, otherwise, all systems for which the HR-V is designed could be properly installed and accommodated.
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor

Head Impact 17.2 Pts
Pelvis Impact 0.2 Pts
Leg Impact 6.0 Pts
| System Name | Collision Mitigation Braking System | ||
| Type | Auto-Brake with Forward Collision Warning | ||
| Operational From | 5 km/h | ||
| PERFORMANCE | | |||
-
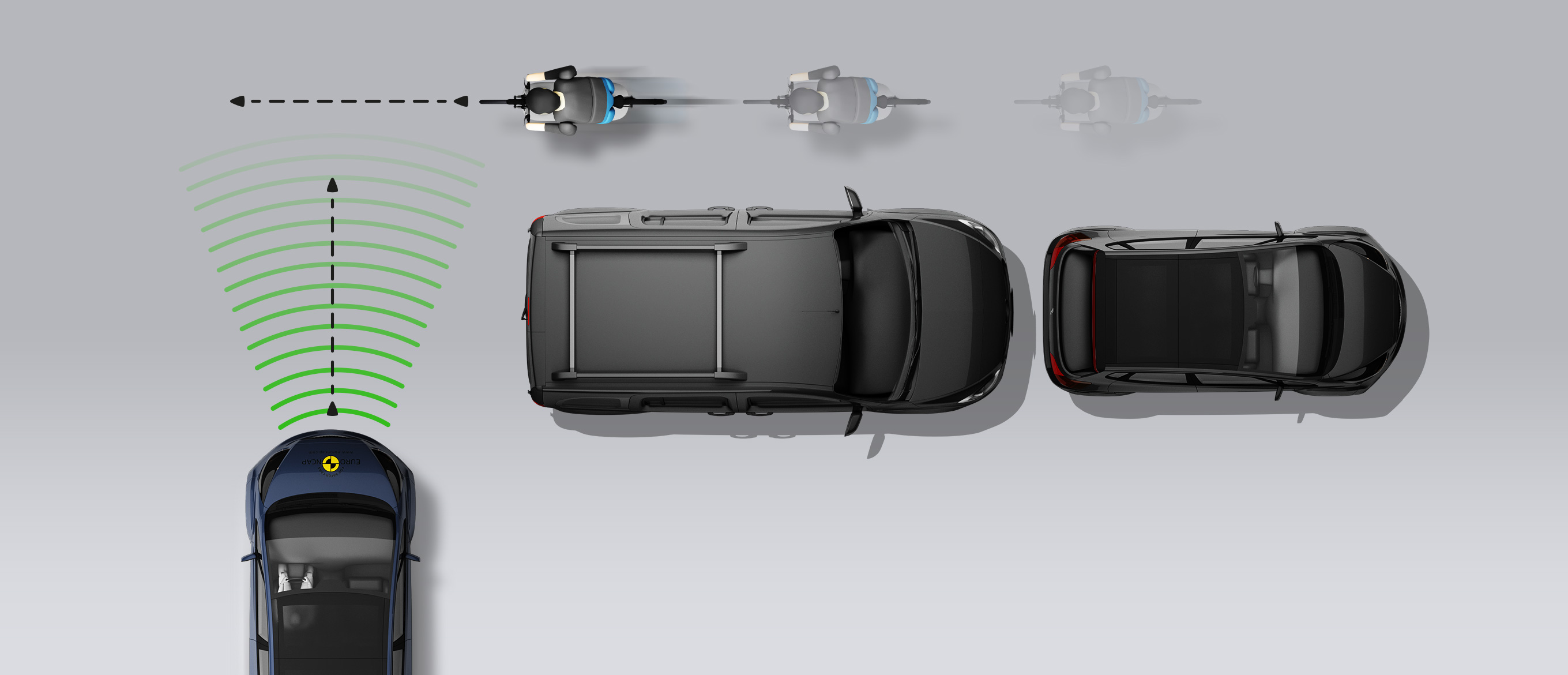
Cyclist from nearside, obstructed view

-
Approaching a crossing cyclist
-
Cyclist along the roadside
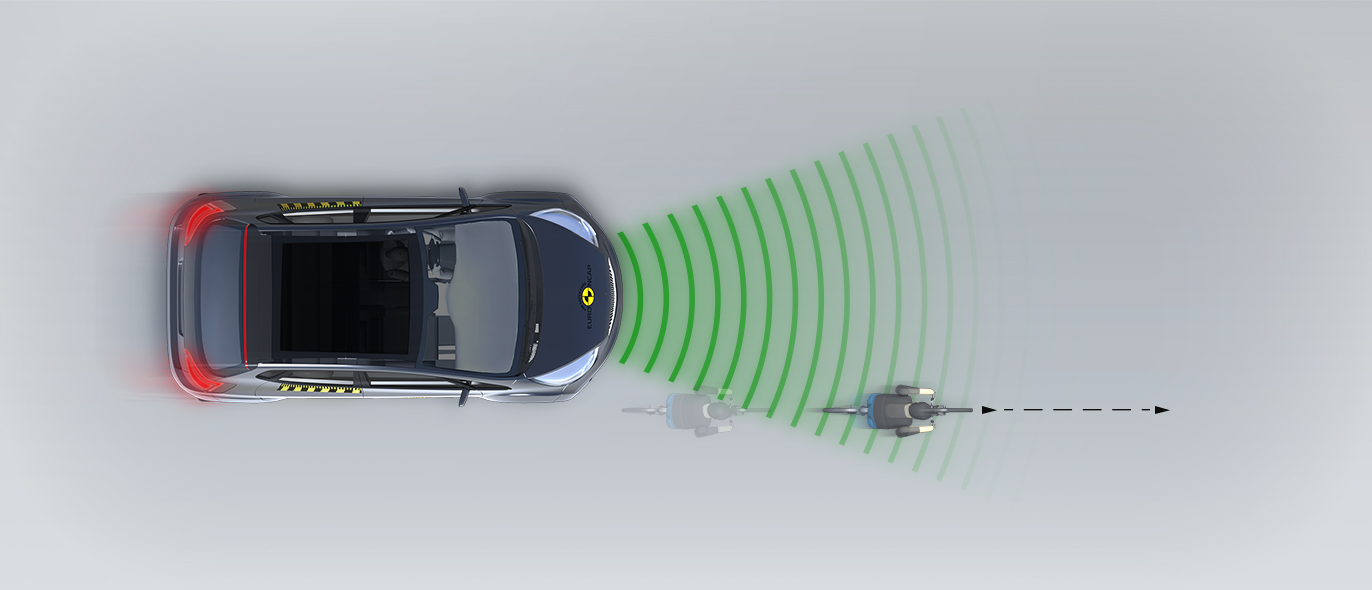
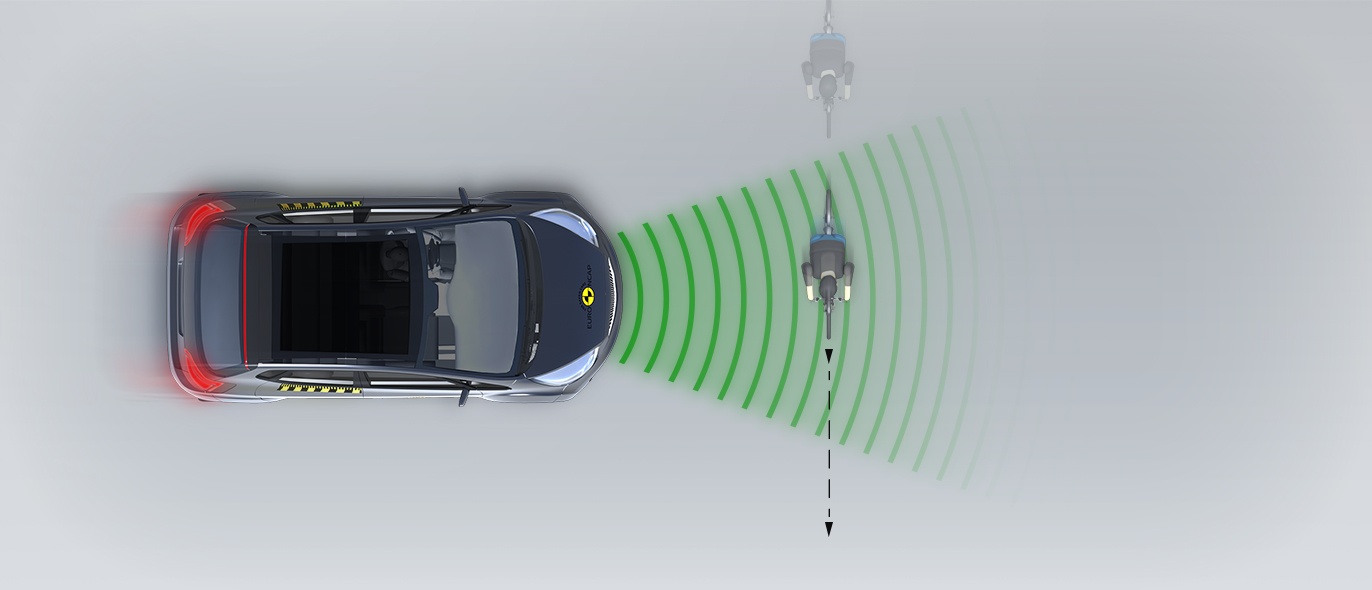
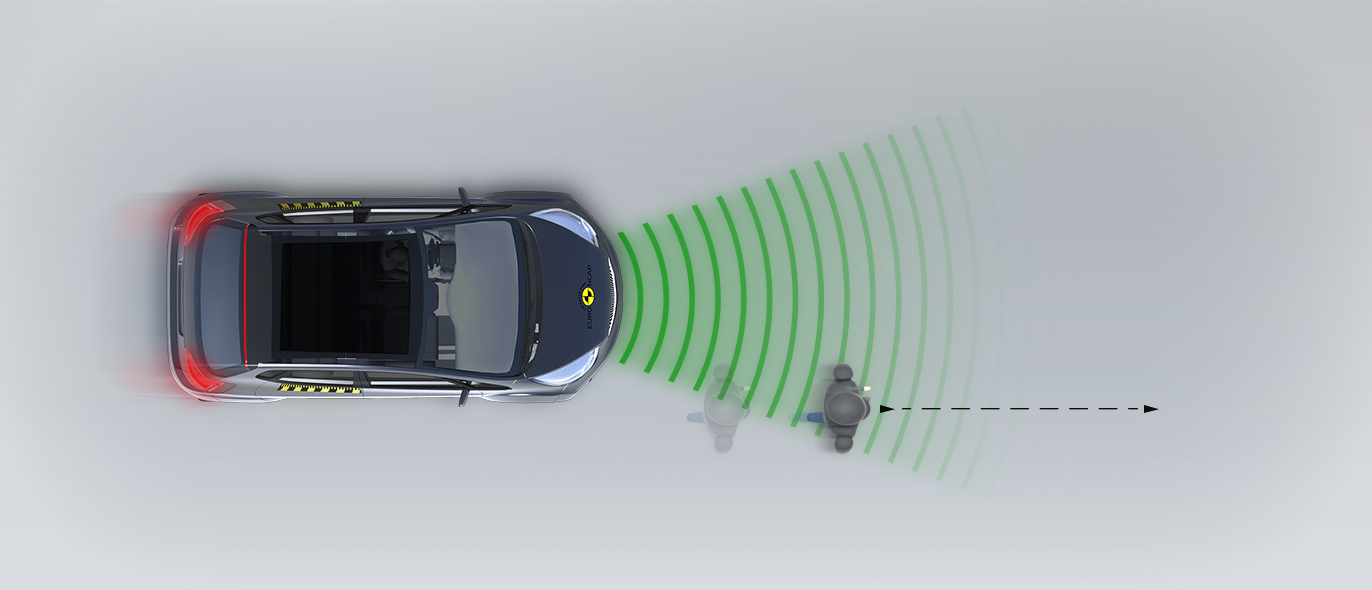
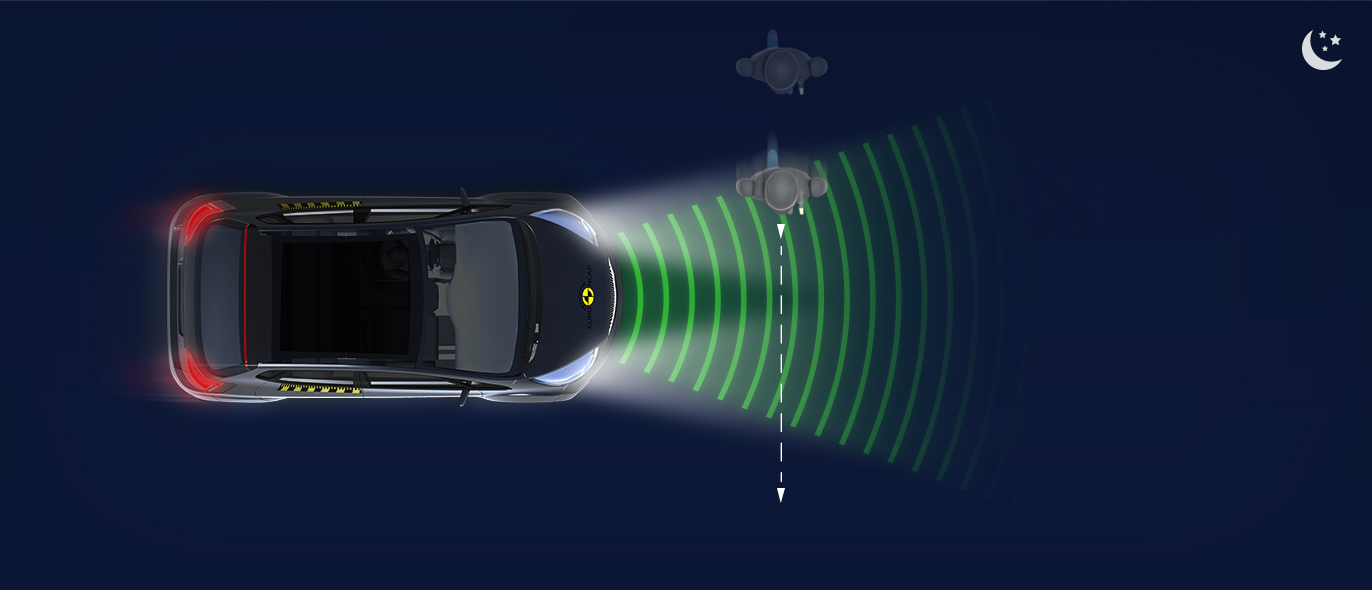
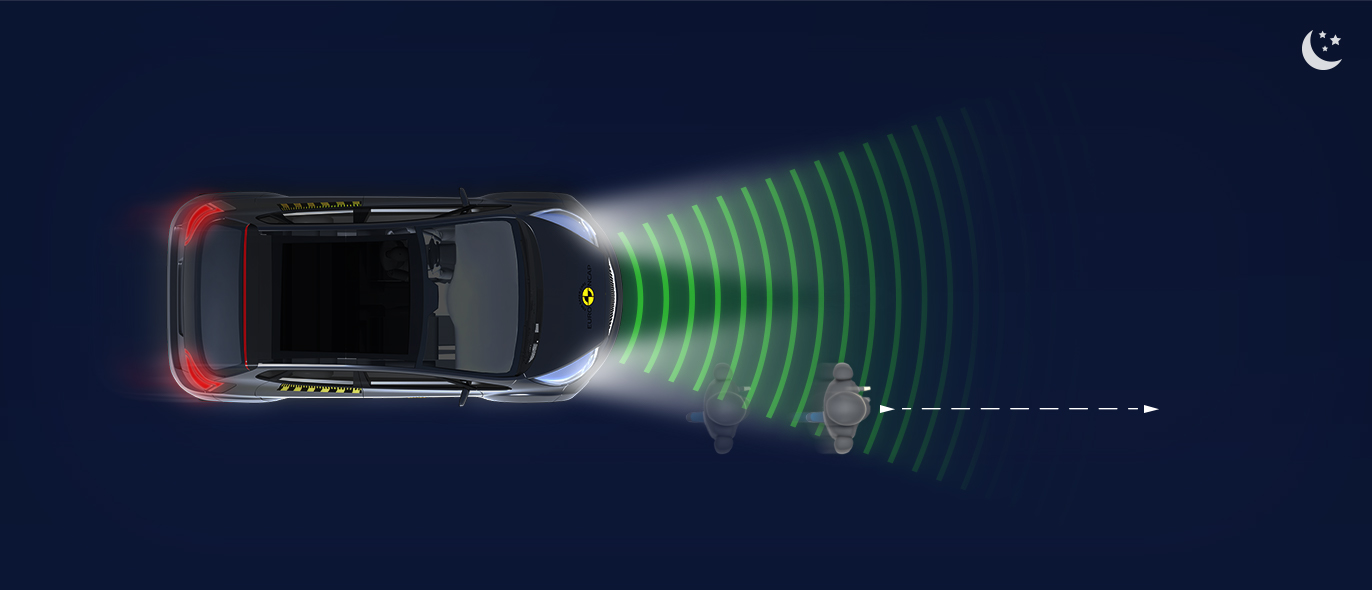
The protection provided to the head of a struck pedestrian was predominantly good or adequate, with some poor results recorded on the stiff windscreen pillars. The bumper provided good protection to pedestrians’ legs at all test points. However, protection of the pelvis was poor almost everywhere along the front edge of the bonnet. The autonomous emergency braking (AEB) system of the HR-V can detect vulnerable road users, as well as other vehicles. In tests of its response to pedestrians, the system performed well, with collisions avoided or mitigated in almost all scenarios. Likewise, the system’s response to cyclists was good.
- Good
- Adequate
- Marginal
- Weak
- Poor
| Speed Limit Information Function | Camera based, subsigns supported |
| Speed Control Function | System advised (accurate to 5km/h) |
| Applies To | Front and rear seats | ||
| Warning | Driver Seat | Front Passenger(s) | Rear Passenger(s) |
| Visual | |||
| Audible | |||
| Occupant Detection | |||
|
|||
| System Name | Road Departure Mitigation System (RDM) |
| Type | LKA and ELK |
| Operational From | 65 km/h |
| Performance | |
| Emergency Lane Keeping | |
| Lane Keep Assist | |
| Human Machine Interface | |
| System Name | Collision Mitigation Braking System | |||
| Type | Autonomous emergency braking and forward collision warning | |||
| Operational From | 5 km/h | |||
| Sensor Used | camera | |||
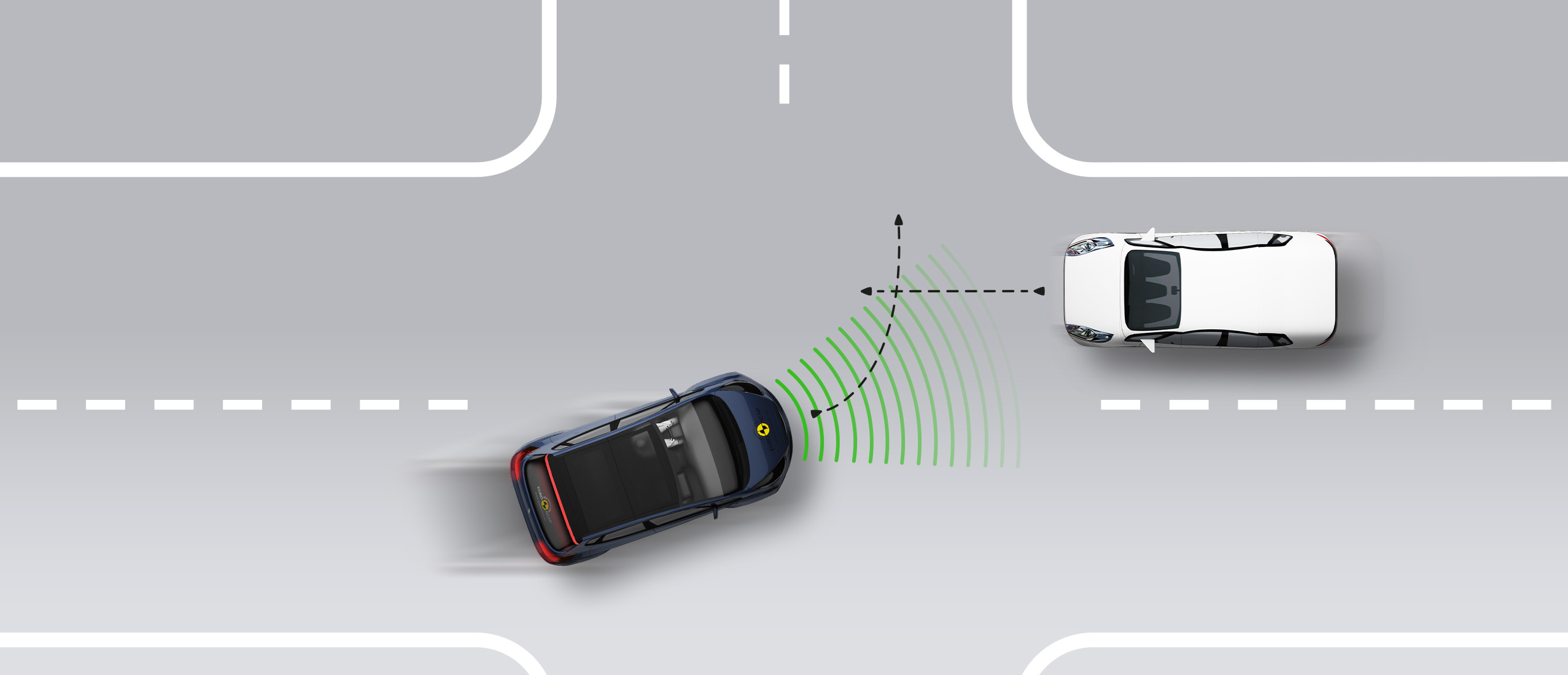
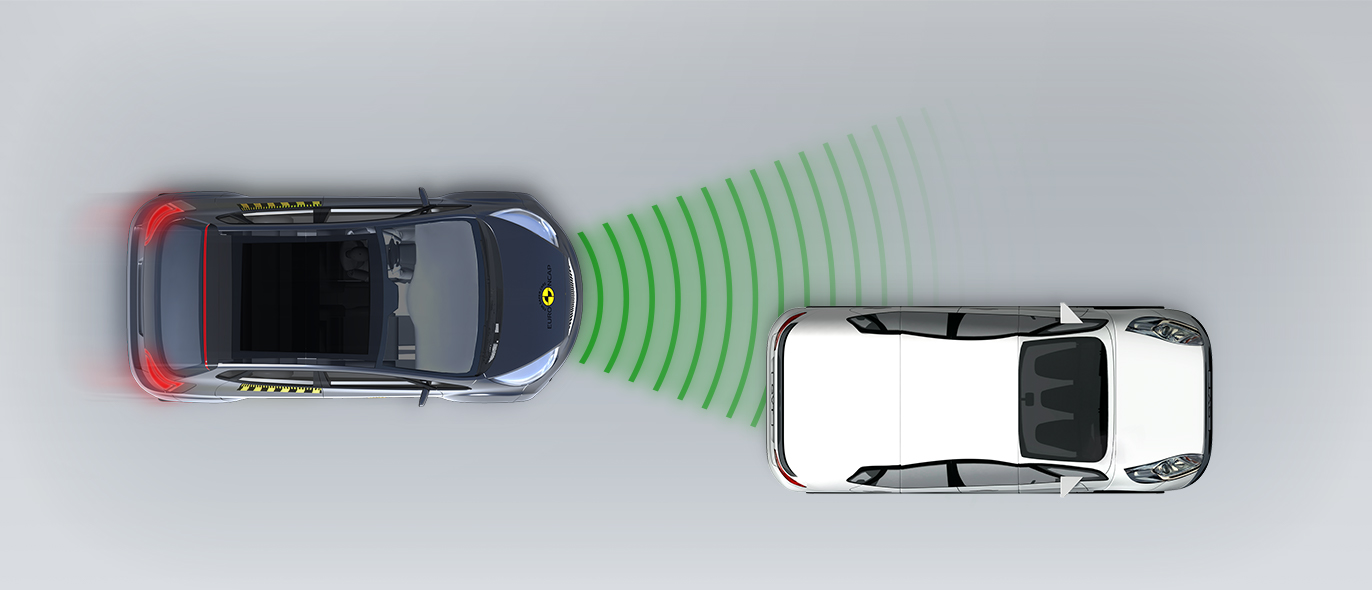
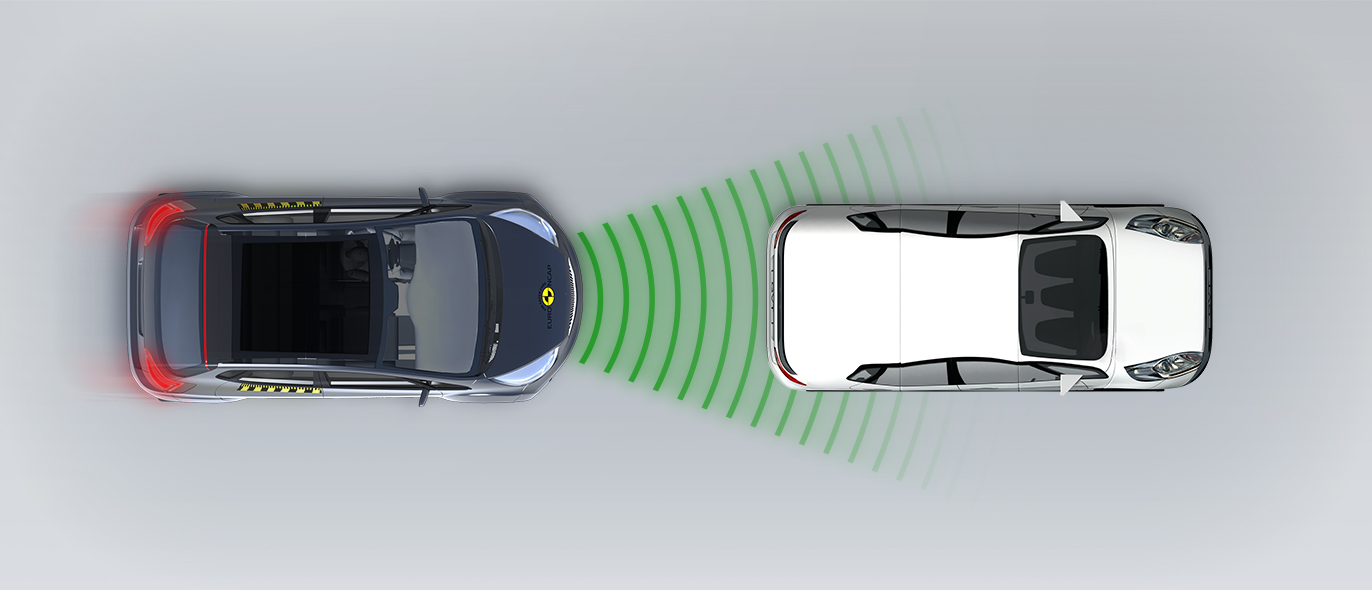
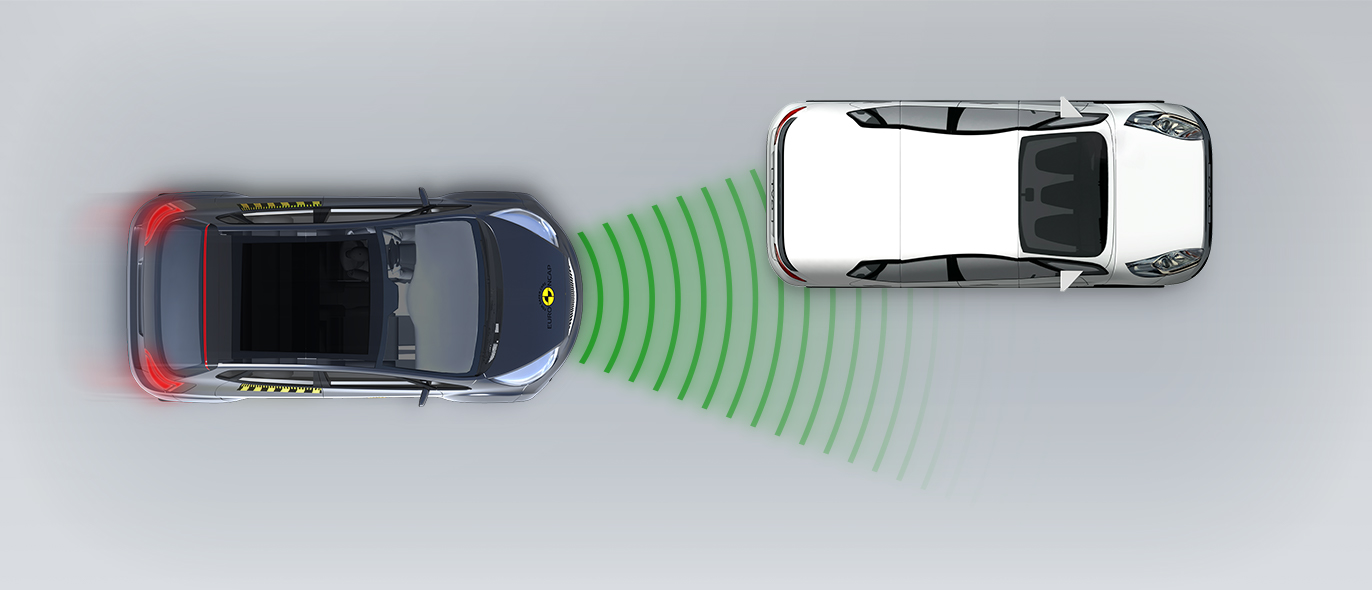
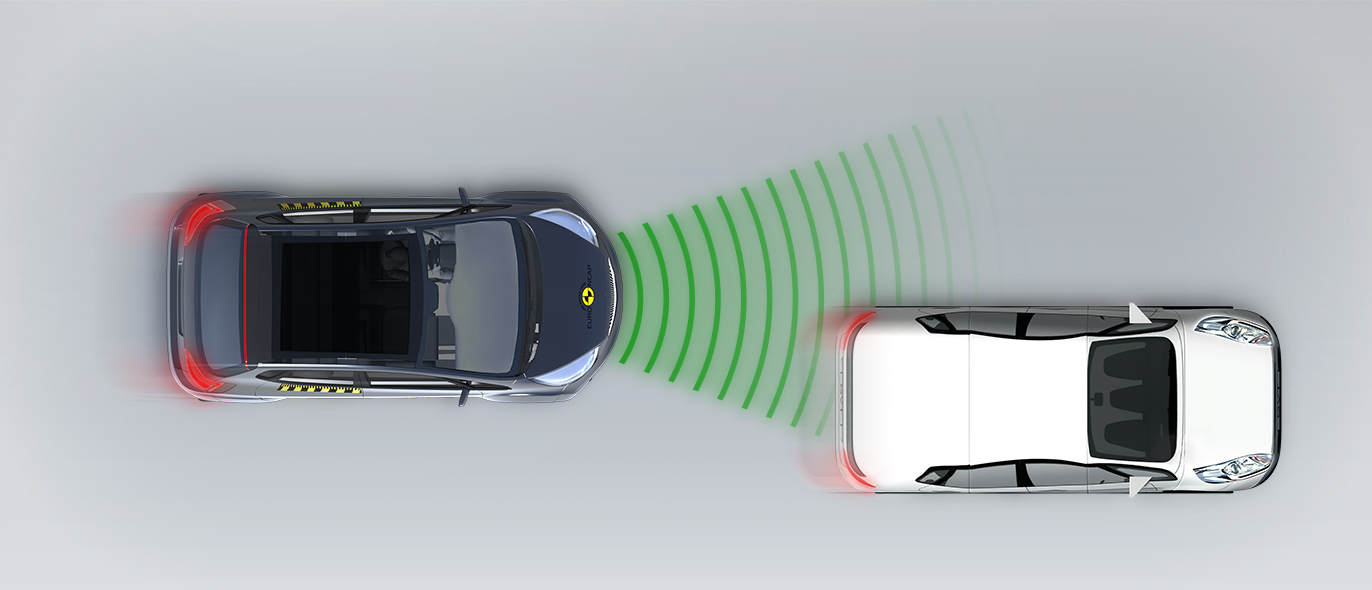
In tests of its response to other vehicles, the autonomous emergency braking (AEB) system performed well. A camera-based speed assistance system identifies the local speed limit. This information is provided to the driver who can choose to allow the car adapt the speed limiter as appropriate. A lane support system gently corrects the vehicle’s path if it is drifting out of lane and can also intervene in more critical situations to avoid road departure, for example. A seat belt reminder is provided for the front and rear seats but there is no system to monitor for fatigued driving.
- Specifications
- Safety Equipment
- Videos
- Rating Validity
Specifications
Tested Model Honda HR-V 1.5 hybrid 'Advance', RHD
Body Type - 5 door SUV
Year Of Publication 2022
Kerb Weight 1389kg
VIN From Which Rating Applies - all HR-Vs
Class Small SUV
Safety Equipment
Note: Other equipment may be available on the vehicle but was not considered in the test year.
Fitted to the vehicle as standard
Fitted to the vehicle as part of the safety pack
Not fitted to the test vehicle but available as option or as part of the safety pack
Not available
Not applicable
Videos
Rating Validity
Variants of Model Range
| Body Type | Engine | Model Name/Code | Drivetrain | Rating Applies | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LHD | RHD | ||||
| 5 door SUV | 1.5 litre hybrid | ADVANCE STYLE | 4 x 2 |  |
 |
| 5 door SUV | 1.5 litre hybrid | ADVANCE | 4 x 2 |  |
 |
| 5 door SUV | 1.5 litre hybrid | ELEGANCE | 4 x 2 |  |
 |
* Tested variant
Find more information in the General Comments section of the assessment
 Share
Share














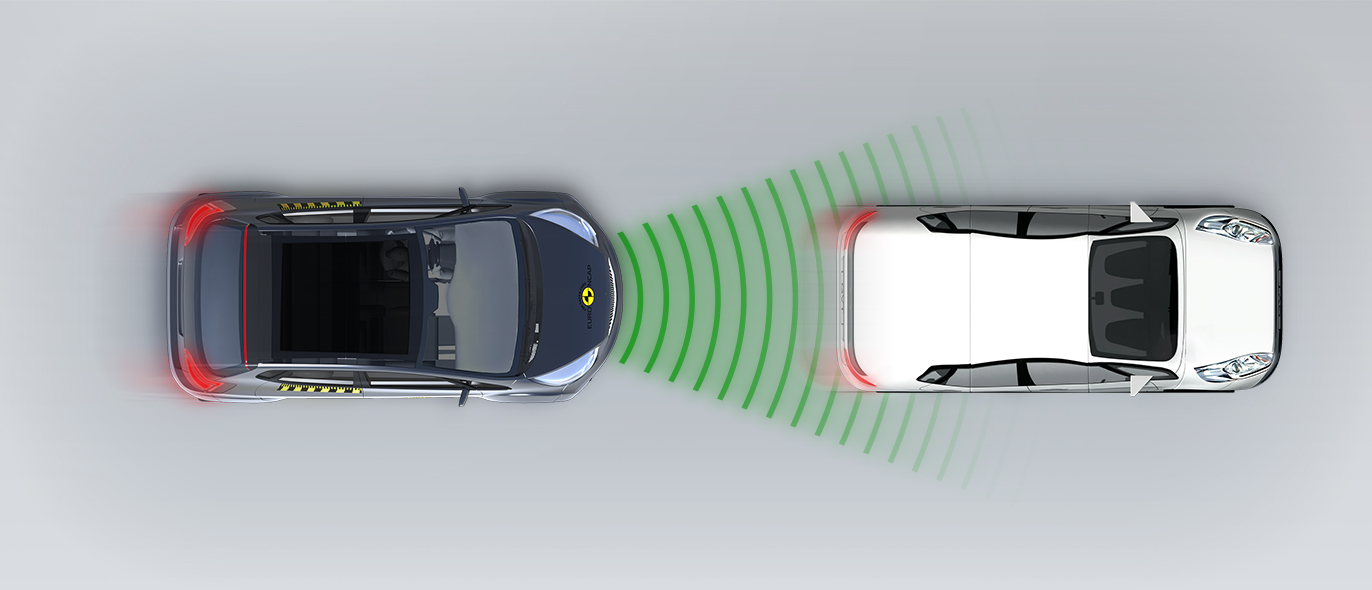
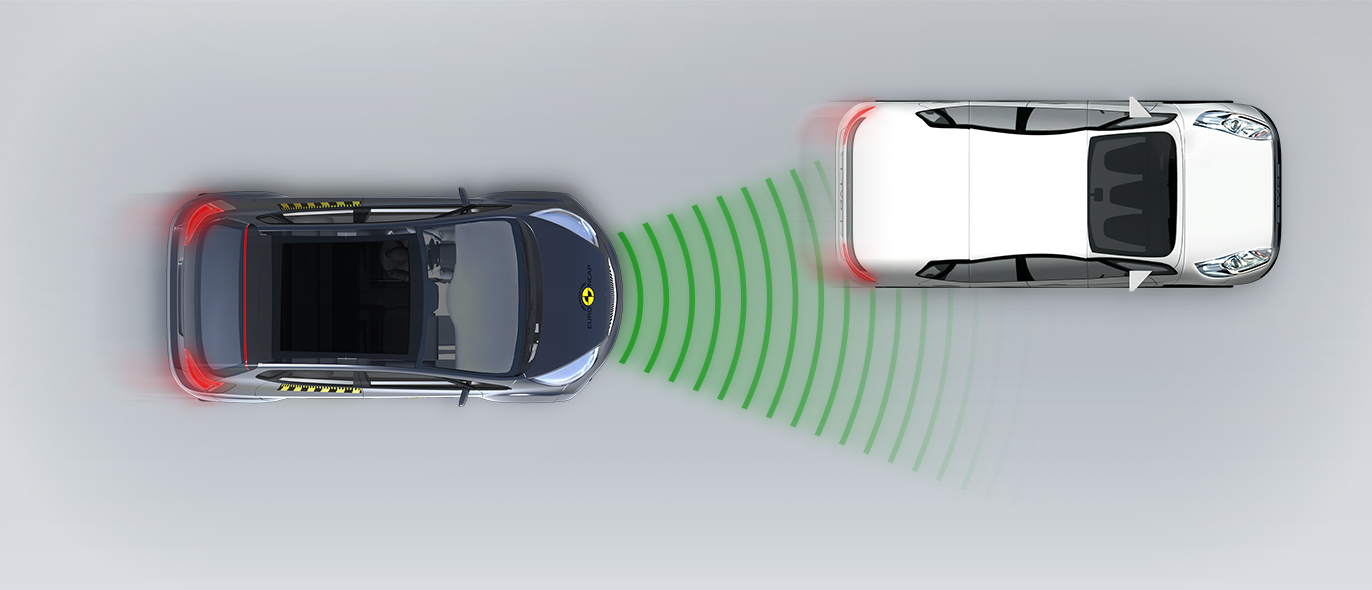
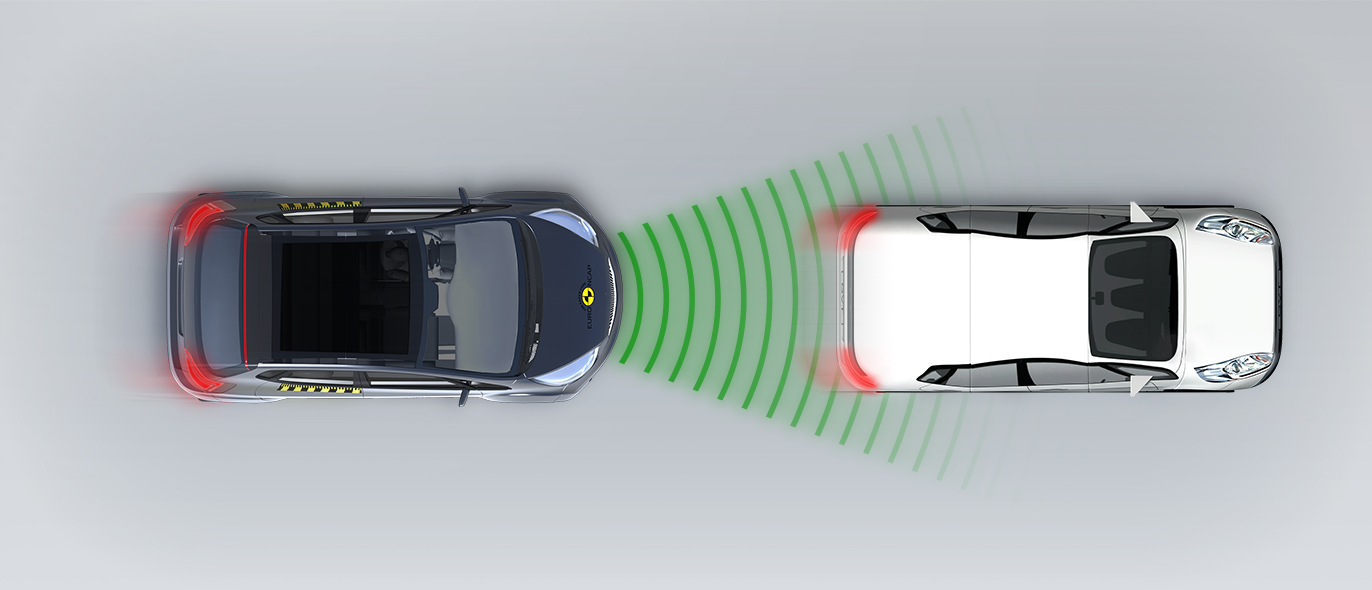

The passenger compartment of the HR-V remained stable in the frontal offset test. Dummy numbers showed good protection of the knees and femurs of both the driver and passenger. Honda showed that a similar level of protection would be provided to occupants of different sizes and to those sitting in different positions. Analysis of the deceleration of the impact trolley during the test, and analysis of the deformable barrier after the test, revealed that the HR-V would be a benign impact partner in a frontal collision. In the full-width rigid barrier test, protection of the chest of the rear passenger dummy was rated as marginal, based on measurements of compression. Otherwise, protection of both dummies was good or adequate. In both the side barrier test and the more severe side pole impact, protection of all critical body areas was good and the car scored maximum points in this part of the assessment. Control of excursion (the extent to which a body is thrown to the other side of the vehicle when it is hit from the far side) was found to be marginal. The HR-V does not have a counter-measure, such as a centre airbag, to mitigate against occupant to occupant injuries in such impacts. Tests on the front seats and head restraints demonstrated good protection against whiplash injuries in the event of a rear-end collision. A geometric analysis of the rear seats also indicated good whiplash protection. The HR-V has an advanced eCall system which alerts the emergency services in the event of a crash but is not equipped with a system to prevent secondary impacts in the event of a collision.